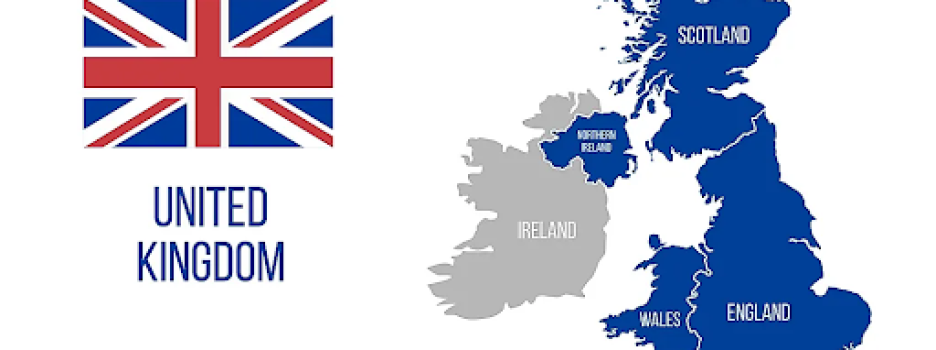
Many people are confused by distinct terms for the political or geographical body that includes England; some people will use Britain and the United Kingdom interchangeably. There are, however, some fundamental differences between England, Great Britain, and United Kingdom.
England
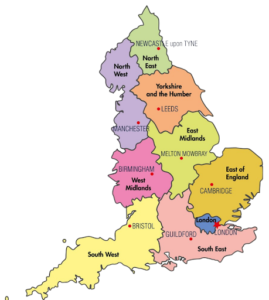
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. England is the largest and most populous nation in the United Kingdom. It is bounded by Wales and the Irish Sea to the west and Scotland to the north. The English Channel, the Straits of Dover and the North Sea separate it from Europe to the east.
Channel Islands such as the Isle of Wight, off the southern mainland in the English Channel, are considered part of England. The Isles of Scilly in the Atlantic Ocean, off the southwestern tip of the continent, are also part of England.
Great Britain
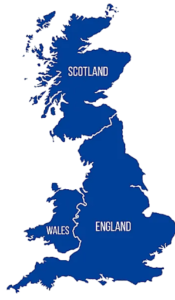
It's the official collective name for England, Scotland and Wales and its associated islands. It does not include Northern Ireland, and should therefore never be used interchangeably with the United Kingdom - something that is seen all too often.
It is located to the east of Ireland and northwest of France in the Atlantic Ocean. The term also includes several offshore islands, including the Hebrides in Scotland.
The United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (to give its full name) refers to the political union between England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland. It is a sovereign state, but the nations that make it up are also countries in their own right.
The United Kingdom is a country that includes England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. While England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland are called countries, there are regulations and policies in these states that are determined by the United Kingdom.
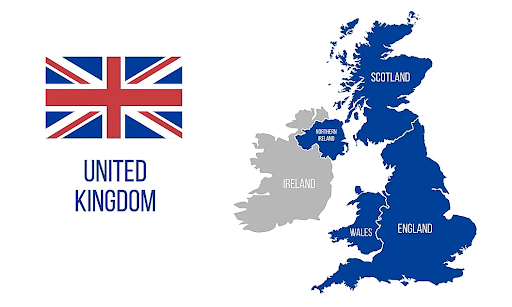
The capital of the United Kingdom is London, although the different countries maintain parliaments in Cardiff (Wales), Edinburgh (Scotland), and Belfast (Northern Ireland). From 1801 to 1922, the United Kingdom also included all of Ireland.
It encompassed the united kingdoms of Scotland and England. They shared monarchs for generations, but were separate entities.
The history
This changed when the Scottish King James Stuart (James I of England and James VI of Scotland) inherited the throne of England from Elizabeth I. James was the grandson of Margaret Tudor, sister of Henry VIII. Since Elizabeth I was childless, this made him her successor.
A century later, her descendant, Queen Anne of England, Scotland and Ireland, would approve the Acts of Union. In both England and Scotland, Parliament passed a treaty of union formalizing a merger of the two states. The result was the United Kingdom of Great Britain. This would later include Ireland, after the Acts of Union of 1800.
The Welsh people were long considered part of the Kingdom of England. They did not establish their own parliament until the late 1990s. The term United Kingdom also includes various dependencies and territories, nations that are politically distinct but depend on the United Kingdom for essential services.
The Channel Islands and the Isle of Man are not part of the United Kingdom, but are Crown Dependencies. Crown Dependencies are three island territories in the British Isles that are autonomous possessions of the British Crown: the Baliwick of Guernsey, the Baliwick of Jersey, and the Isle of Man.
They are neither part of the United Kingdom nor are they British Overseas Territories. They have the status of "territories for which the United Kingdom is responsible," rather than sovereign states. As a result, they are not members of the Commonwealth of Nations.
The Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations is a voluntary association of 52 states or countries that were formerly part of the British Empire. This does not include the United States.
- 16 Commonwealth of Nations members recognize the Monarch of the United Kingdom as their own king or queen, but remain politically independent. These are Commonwealth realms.
- 33 other Commonwealth countries are republics, which means that they do not recognize a monarch. However, they still participate in the partnership.
The Commonwealth has no constitution. The Singapore Declaration of Commonwealth Principles, however, states that the Commonwealth is "a voluntary association of independent sovereign states, each responsible for its own policies, consulting and cooperating in the common interests of their peoples and in promoting international understanding and world peace."